Do you want to limit login attempts in WordPress? If you are looking for a simple guide, keep reading this article.
Limiting the number of login attempts in WordPress is one of the simplest ways to strengthen login security and protect your WordPress site from brute force attack attempts.
When a bot or malicious user makes many failed login attempts, they try to guess your username and password until they gain unauthorized access.
By applying a limit on the number of login attempts in WordPress, you immediately reduce the risk of repeated login attempt abuse and block attackers before they reach your site.
This guide explains how login attempt limits work, why failed login attempts in WordPress are dangerous, and how to limit login attempts in WordPress using different methods to keep your website secure.
First, let’s see what does limit login attempts mean.
Table of Contents
What Does “Limit Login Attempts” Mean in WordPress?
Limiting login attempts in WordPress means setting a limit on how many times a user or bot can attempt to log in to your WordPress site before being temporarily blocked.
When there are many failed login attempts, it often signals a brute force attack where automated bots try hundreds of usernames and passwords to gain access to your site.
By limiting the number of login attempts on your WordPress login page, you prevent attackers from repeatedly attempting to log in and strengthen your overall login security.
Here is what this process involves:
- It monitors every login attempt on your WordPress login screen and records the number of failed attempts.
- Once the number of failed login attempts exceeds your configured limit, the user or bot is locked out for a specified period to protect your site.
- The lockout is based on the IP address and blocks login attempts to your WordPress site.
- A login-limiting rule prevents unauthorized access attempts and improves website security by limiting login attempts.
- With a security plugin like Limit Login Attempts Reloaded, Wordfence, or a similar WordPress plugin, you can automatically block malicious users and secure your WordPress admin from brute force attack bots.
- Limiting login attempts helps legitimate users while protecting your WordPress site from unauthorized access.
Why You Should Limit Login Attempts on WordPress
Limiting login attempts on your WordPress site is one of the simplest and most effective ways to strengthen login security and block unauthorized access before it becomes a problem.
When attackers attempt to log in repeatedly, they often rely on brute-force bots that submit unlimited login attempts until they find the correct username and password.
By limiting login attempts on your WordPress login page, you protect your site and maintain a secure WordPress installation for genuine users.
Key reasons to implement login limiting:
- It prevents brute-force attack bots from repeatedly attempting to log in by enforcing a per-session login limit based on failed login attempts.
- When activity logs show many login attempts from the same IP, a limit-login-attempts plugin can automatically lock that user and secure your site.
- Limiting login attempts helps protect your WordPress admin area by reducing the risk of unauthorized access.
- A plugin like Limit Login Attempts Reloaded or WP Limit Login Attempts helps you quickly enable limit login rules and keep your site secure.
- Login limiting helps keep your website secure, even without a plugin, since WordPress lets you implement basic rules manually if needed.
- Limiting failed login attempts in WordPress improves site security and provides essential protection against malicious users.
How to Limit Login Attempts in WordPress
We will be using a plugin called Limit Login Attempts Reloaded. First, install and activate this plugin on your WordPress website.
After the activation, you can see the plugin’s settings on the left-hand side.
Now open the settings.
The configuration options are simple. Here is how you can do it. The first option you see will help you choose the lockout.
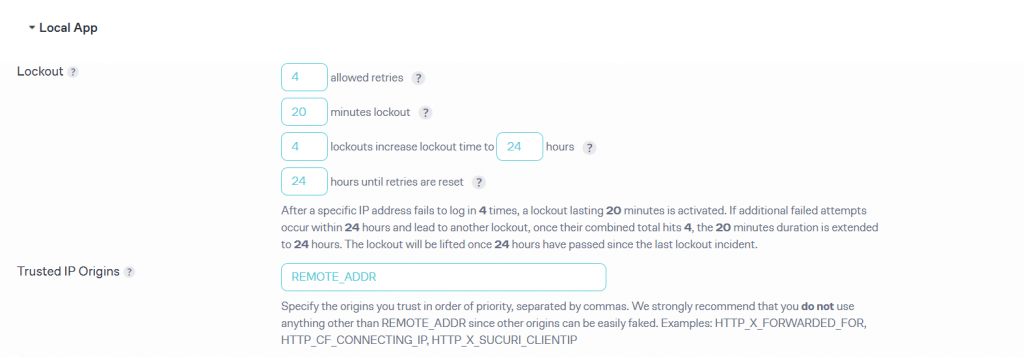
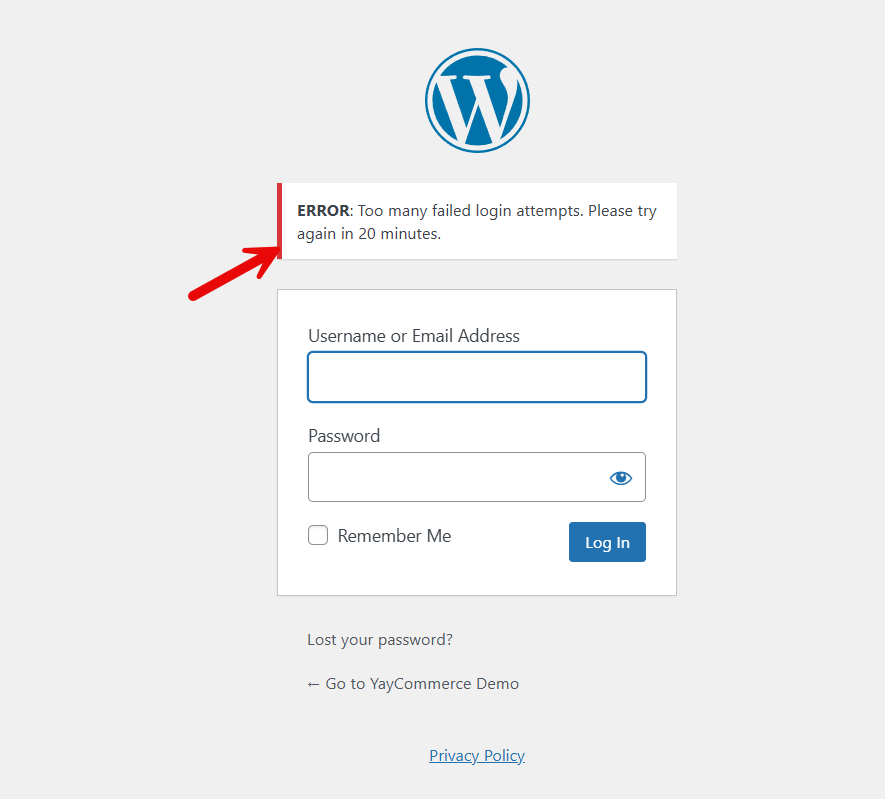
The default options are okay for any website. What it does is that when someone tries to log in to your website and makes four failed attempts, their IP address is flagged for 20 minutes. During those 20 minutes, they can’t log in again.
After 20 minutes, they can try to log in. If they still enter the login credentials incorrectly four more times, their IP address is banned for the next 24 hours.
This is a decent setup for a membership website or personal blog.
Next, move to the general settings.
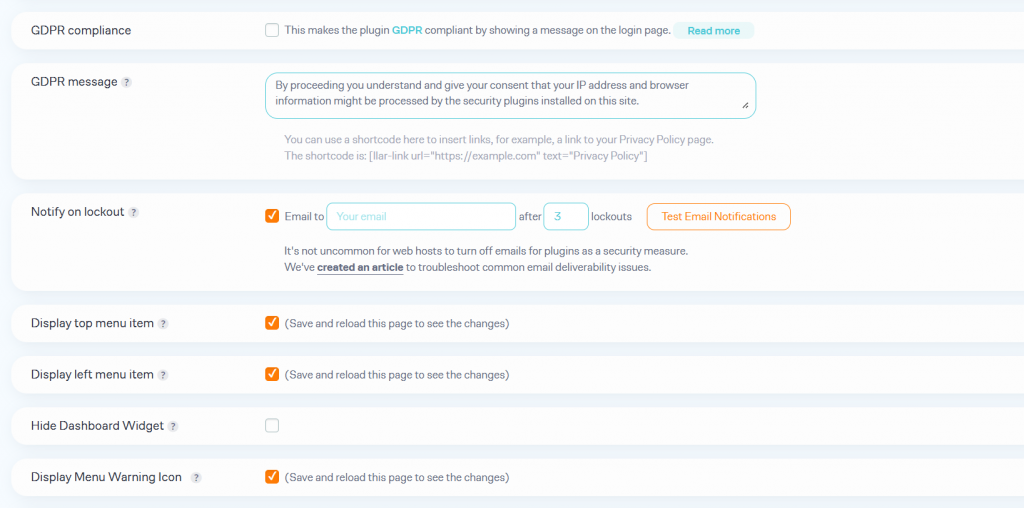
You can make the plugin GDPR-compliant, tweak the message, configure the plugin’s display options, and more. Once you are done with the configuration options, save the changes. You can try logging in to the site from a private window. And you will see this message.
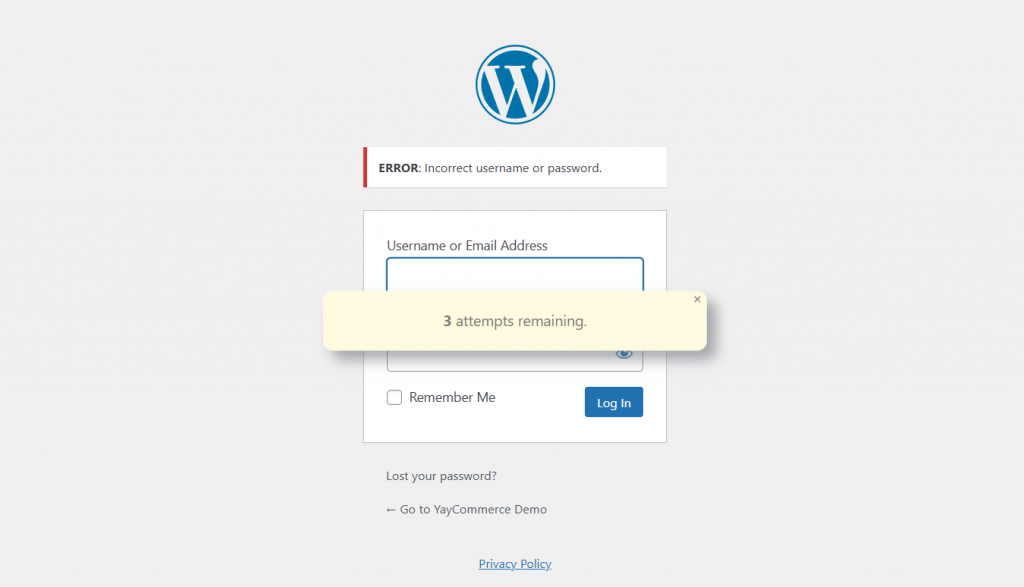
When someone uses all four retries, the plugin will display this message.
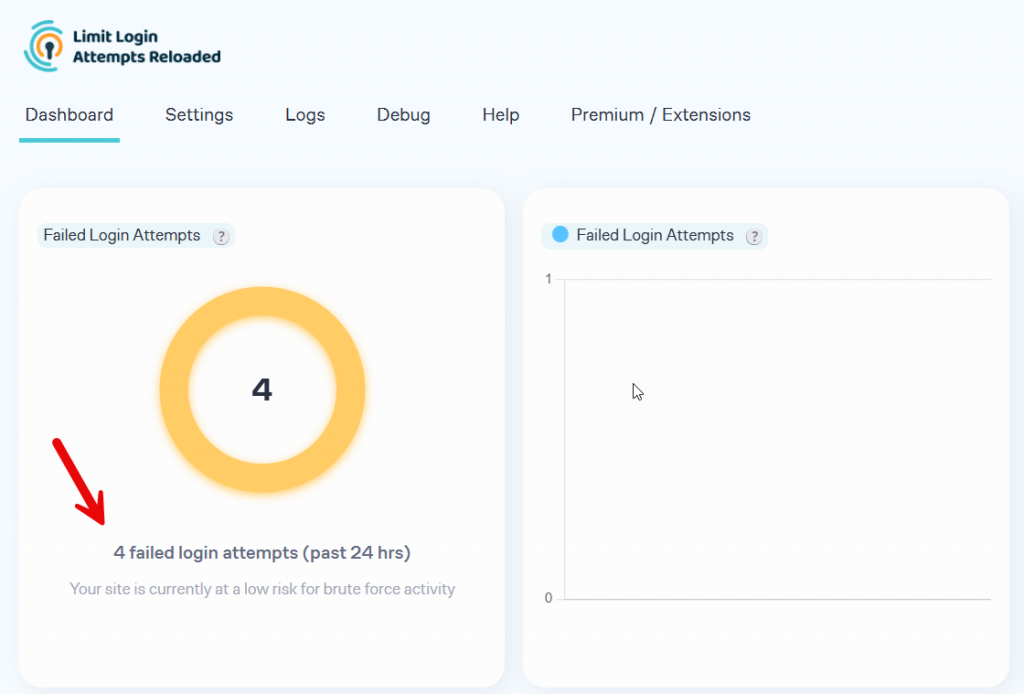
In the plugin’s dashboard, you can view the total number of login retries in the last 24 hours.
That’s it!
This is how you can limit login attempts in WordPress.
Best Login Security Practices to Protect Your WordPress Site
Strengthening login security on your WordPress site requires more than simply trying to limit login attempts in WordPress.
While limiting login attempts on your WordPress login page is essential, there are several additional measures that further fortify your site and reduce the risk of brute-force attacks.
These measures make unauthorized access to your WordPress admin area significantly more difficult, even if attackers repeatedly attempt to log in.
Here are the most effective practices:
1. Use Strong, Unique Usernames and Password
A large majority of failed login attempts in WordPress occur because attackers exploit weak usernames and passwords. Strong credentials protect your site and reduce the likelihood that someone can trigger the wrong password too many times in your login process.
2. Enable Two-Factor Authentication (2FA)
Adding an extra authentication layer helps secure your WordPress site even if a password is compromised. When enabled, a bot cannot bypass the second factor, further reducing attempts at unauthorized access.
3. Limit Login Attempts Using a Security Plugin
A limit login attempts plugin, such as Limit Login Attempts Reloaded or WP Limit Login Attempts, provides comprehensive login protection. These tools can automatically lock out users after multiple failed login attempts and display a message on your login screen.
Installing the plugin from the WordPress dashboard is one of the easiest ways to limit login attempts.
4. Change Your Login URL
Attackers often reach your login page simply because WordPress allows a default URL. Using a custom login URL makes brute force attack patterns less effective and helps fortify your site from automated scripts.
5. Monitor Activity Logs
Activity logs help you track WordPress login attempts, detect many failed login attempts, and identify whether a legitimate user or attacker is trying to log in. This level of monitoring supports site security and user safety.
6. Restrict Access With IP-Based Rules
Login limiting can go beyond simply using limit login attempts plugins. You can add server-level rules to restrict access to your WordPress admin area by IP address. This adds another way to limit unauthorized access to your WordPress site.
7. Keep All WordPress Plugins Updated
Whether you use a security plugin or any other tool, keeping every plugin you want to install updated ensures you are not exposed to vulnerabilities attackers frequently exploit.
By applying these login protection practices and using limit login attempts plugins where needed, you significantly strengthen WordPress security and secure your site against malicious actors.
These steps ensure that even if someone attempts to gain access repeatedly, the user is locked out before any damage occurs.
Frequently Asked Questions
Now, let’s take a look at some frequently asked questions about this topic.
How do login attempts in WordPress affect the overall login security of my WordPress site?
Limiting login attempts in WordPress is crucial because unlimited attempts allow attackers to repeatedly attempt to log in. When your WordPress site logs many failed login attempts, it becomes vulnerable to a brute-force attack. Implementing login security measures ensures that login attempts on your WordPress site trigger protection before credentials are guessed.
Why should I limit the number of login attempts on my WordPress site?
Login attempts in WordPress are unrestricted by default, allowing a bot to make many failed attempts rapidly. When you limit login attempts, you implement a robust login policy that blocks attackers and protects your site. This approach prevents failed login attempts in WordPress from escalating into unauthorized access.
Can I limit login attempts in WordPress without a plugin?
Yes. You can reduce login attempts on your WordPress site without a plugin by using server-level rules, security configurations, or custom code. However, this can be complex. A WordPress plugin designed for limiting the number of login attempts is easier to manage and allows you to activate the limit login feature safely.
What is the best limit login attempts plugin for WordPress login protection?
The most widely used option is the Limit Login Attempts Reloaded plugin, but many other security tools support similar controls. A WP limit login attempts plugin adds login limiting features that protect your site by detecting many failed login attempts and locking out suspicious WordPress users before they compromise site security.
How does a bot trigger many failed login attempts on my WordPress login page?
A bot crawls the internet to find your login page and performs automated requests to guess passwords. This results in many failed login attempts, which can escalate into a brute-force attack if attempts are not restricted. Using a limit login attempts plugin ensures a user is locked after entering the wrong password too many times.
Where do I install the plugin if I want to use the WP Limit Login Attempts plugin?
You can install the plugin directly from your WordPress admin panel or upload it to the plugin folder manually. Once installed, activate the limit login feature to enforce login limitation rules. Login attempts is a simple setting to configure but provides your site with strong protection.
How do I protect my site from unauthorized access to your WordPress login area?
Start by enabling a limit-login-attempts plugin to reduce the number of login attempts. This ensures that attempts to access your WordPress site are monitored and restricted, preventing unauthorized access. Combine this with other security practices—such as hiding the login URL or reviewing activity logs to fortify your overall security posture.
Conclusion
Limiting login attempts in WordPress is one of the simplest and most effective ways to strengthen login security and protect your WordPress site from failed login attempts and brute-force attacks.
By limiting login attempts on your WordPress site, you immediately reduce the risk of unauthorized access and improve overall site security. Using a dedicated WordPress plugin, such as Limit Login Attempts Reloaded or a similar WP limit login attempts plugin, makes the entire login limitation process easier to configure and manage.
These tools lock out users after repeated failed login attempts in WordPress, preventing bots and malicious actors from repeatedly attempting to log in. Whether you enforce login limits with plugins or set up restrictions without them, adding this level of login protection is essential for safeguarding your WordPress website.
When you combine login attempt restrictions with other best practices such as securing your login URL, reviewing activity logs, and maintaining broader WordPress security measures, you fortify your site and provide it with a robust defensive layer against unauthorized access attempts.
By implementing these measures today, you can secure your WordPress site, reduce vulnerabilities, and keep both administrators and genuine users safe throughout the login process.
Do you know any other WordPress security practices?
Let us know in the comments.
